Most visitors come to your site through search engines like Google, Bing, and Yahoo. However, you must target the right keywords to generate and increase organic traffic to your site. That is why keyword research is a vital component of online content marketing. In this post, I will discuss all you need to know about keyword research.
What are Keywords?
Keywords are words, terms, queries, or phrases users enter in search engines to find appropriate information online. They help searchers find relevant sites or web pages while aiding businesses to target the right audience.
Finding the right keywords is critical for SEO. Targeting the right keywords helps you rank higher in search engine result pages and ensures you reach out to your target audience.
What is Keyword Research?
Keyword research is the process or practice of finding, analyzing, and strategically using the right keywords in your content to achieve a higher rank in search engine result pages (SERPs). It ensures you are targeting only those keywords that will benefit your business in achieving marketing goals.
In simple words, keyword research is the practice of choosing a set of keywords for your content so that the content focuses on those keywords and satisfies both users and search engines.
Importance of Keyword Research for SEO
Keyword research is beneficial for SEO for several reasons, such as:
- You learn about your target audience by discovering what they are searching online.
- It helps you generate new content ideas.
- It enables you to identify content gaps.
- You find out the search intent or the type of content your target audience expects.
- It gives you a better understanding of your competition.
Three Steps of Keyword Research
Step 1: Discovering Keywords
The first step to keyword research is discovering appropriate keywords that will likely bring traffic to your site. However, finding keywords is tricky. With proper strategy, you may avoid choosing keywords that are either highly competitive or have zero search volume.
Therefore, it is critical to follow a strategy for discovering the right keywords for your business.
Identify Seed Keywords to Generate Keyword Ideas
Before generating keyword ideas, you need a starting point, i.e., a seed keyword. A seed keyword is a broader keyword used as a starting point to find more keyword ideas. It is a short-tail keyword and usually consists of one to three words. For example, if you have a marketing company, your seed words would be:
- Social media marketing
- Email marketing
- Influencer marketing
- Electronic media marketing
The simplest way to find seed keywords is brainstorming. Ask yourself the following questions to come up with a list of seed keywords:
- What are the services or products you are selling?
- What are the main topics on your website?
- What keywords do people use for searching topics related to your business?
Although brainstorming involves guesswork, the purpose of finding seed keywords is to have an initial set of keywords, using which you can explore more keyword ideas.
Besides brainstorming, I suggest researching your target audience for the seed keywords. Define your target audience and discover their problems, queries, interests, and concerns. Find out the terms they use to search for products or services you offer. Additionally, discover terms they use to learn more about your products or business.
One way to research the target audience is to look into blog comments, social media comments, feedback, or any other correspondence they have with you. You can also conduct surveys or look into questions your target audiences ask on different forums and groups.
After you have a list of seed keywords, you can generate keyword ideas using the following methods, all of which are explained in detail below:
- Use keyword research tools.
- Find trending topics on Q&A sites and discussion forums like Reddit, Quora, etc.
- Use auto-complete or suggest features of top search engines like Google, Yahoo, and YouTube.
- Use the related search feature of Google.
Use Keyword Research Tools
Now that you have identified seed keywords, you can utilize keyword research tools to generate keyword ideas. Below are popular keyword research tools digital marketers use:
Keyword research tools give an exhaustive list of keyword suggestions related to your seed keyword that people search for. The most significant advantage of using such tools is that you get an estimate of how many searches each keyword generates in a month. This information is critical because you would not want to target keywords that are either highly competitive or have a very low search volume.
To generate keyword ideas, type each seed keyword in the keyword research tool and copy the suggestions relevant to your business. Below is the screenshot of keyword suggestions in SEMrush's Keyword Magic Tool.
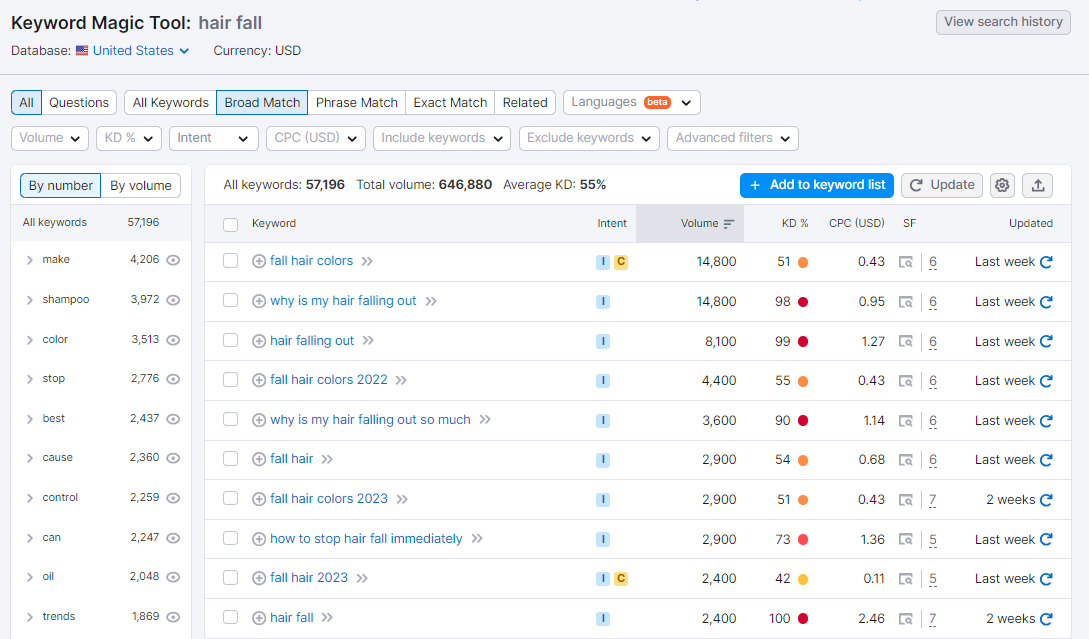
As shown in the screenshot above, you get a list of:
- Keyword suggestions.
- Keywords related to the seed keyword. The related terms may not necessarily include the seed keyword.
- Question style keyword ideas.
- Preposition style keyword ideas.
- Keyword suggestions that indicate comparison.
For each keyword, the following parameters are also shown:
- Monthly search volume.
- Average cost per click or CPC that you may have to pay Google for an Ad.
- Paid difficulty, i.e., the estimated competition in paid search.
- Search difficulty, i.e., the estimated competition in organic search.
All of these parameters help you choose the right keywords to target. I have discussed these parameters in detail later in this post.
Use Google Search
Google search is ideal for generating keyword ideas using seed keywords. The only downside is that you do not know the search volume of different keywords.
The following are the three ways you can use Google search to generate keyword ideas:
Autocomplete or Google Suggest: If you type a seed keyword in the Google search bar, the search engine will suggest a list of keywords people are searching, as shown below:
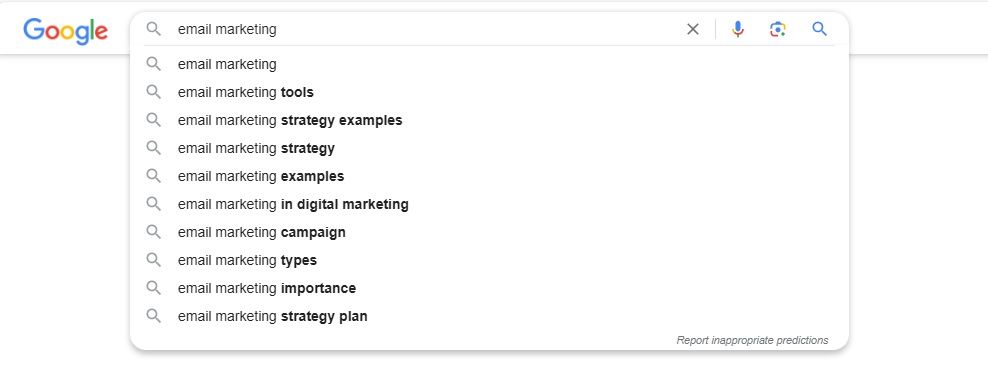
Google suggestions are best to add to your keywords list as Google suggests those keywords that many people use for searching for information online.
People Also Ask: Another valuable feature of Google search that you can use for keyword research is the 'People Also Ask' snippet. In this snippet, Google suggests popular queries people ask about the seed keyword you typed in the search bar.
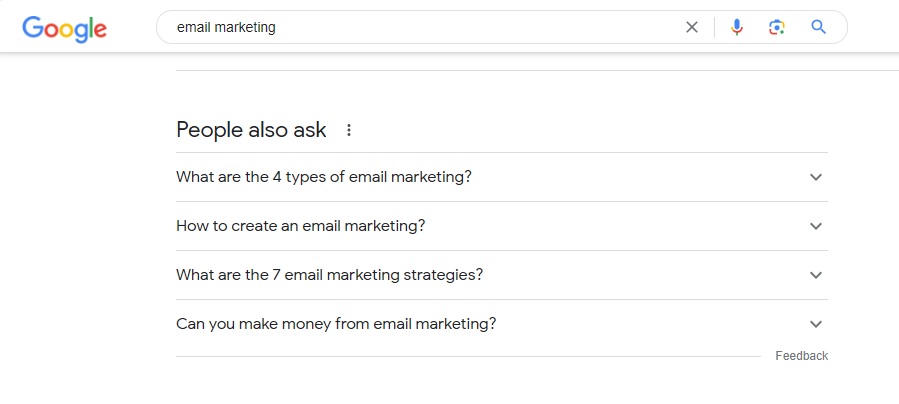
The question queries in this snippet are best for long-tail keywords. An exciting feature of the 'People Also Ask' snippet is that the list of suggestions will expand if you click on one of the questions. In other words, you can generate an unlimited list of suggestions using this snippet.
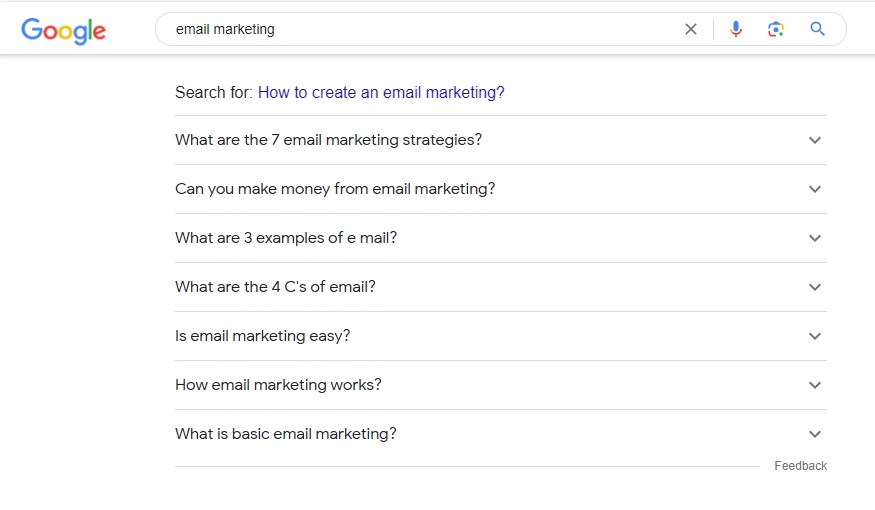
Other Searches: The third feature of Google search that is helpful for keyword research is 'other searches'. It is displayed at the bottom of the first page of Google search results. It is similar to autocomplete, and most suggestions would be the same as in autocomplete. However, a few suggestions would be unique that you can add to your keywords list.
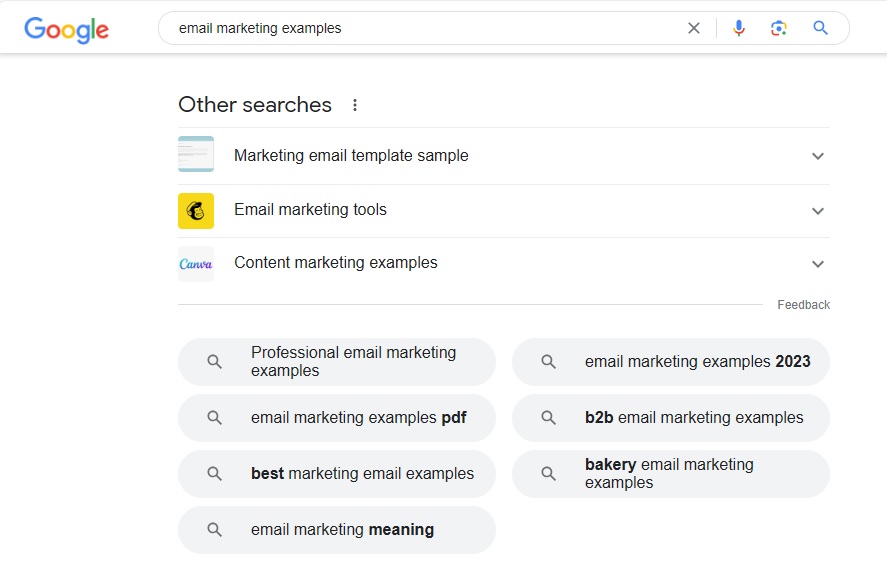
Auto Complete Feature of Search Engines and Sites
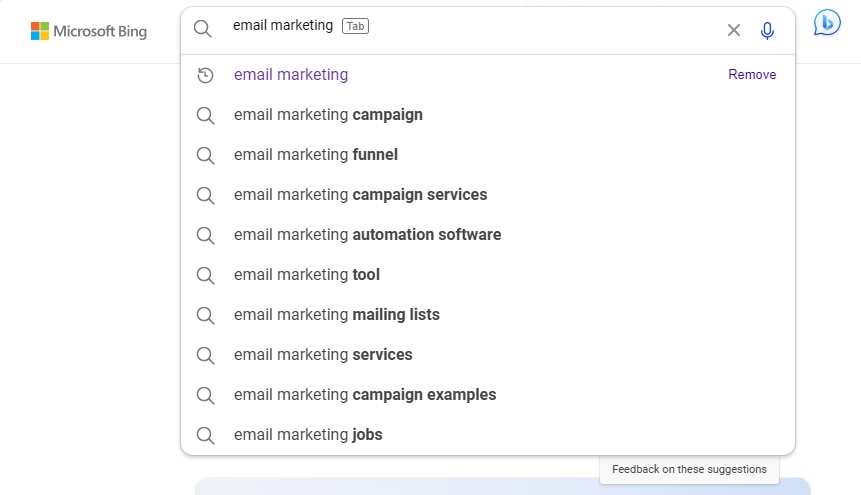
Like Google, most other search engines, like Yahoo, Bing, and YouTube, also have an autocomplete feature that you can use to get keyword suggestions.
As shown in the screenshot below, the suggestions in Bing differ from those in Google search for the same keyword, i.e., email marketing.
Therefore, you can use multiple search engines to generate keyword ideas to diversify keyword research. These search engines also have a 'related searches' feature, and a few have a 'People Also Ask' feature. Below is a screenshot of the Yahoo search:
Using autocomplete of multiple search engines can be time-consuming. To save time and energy, you can use Soovle, a popular tool for generating autocomplete suggestions for top search engines and sites in one place.
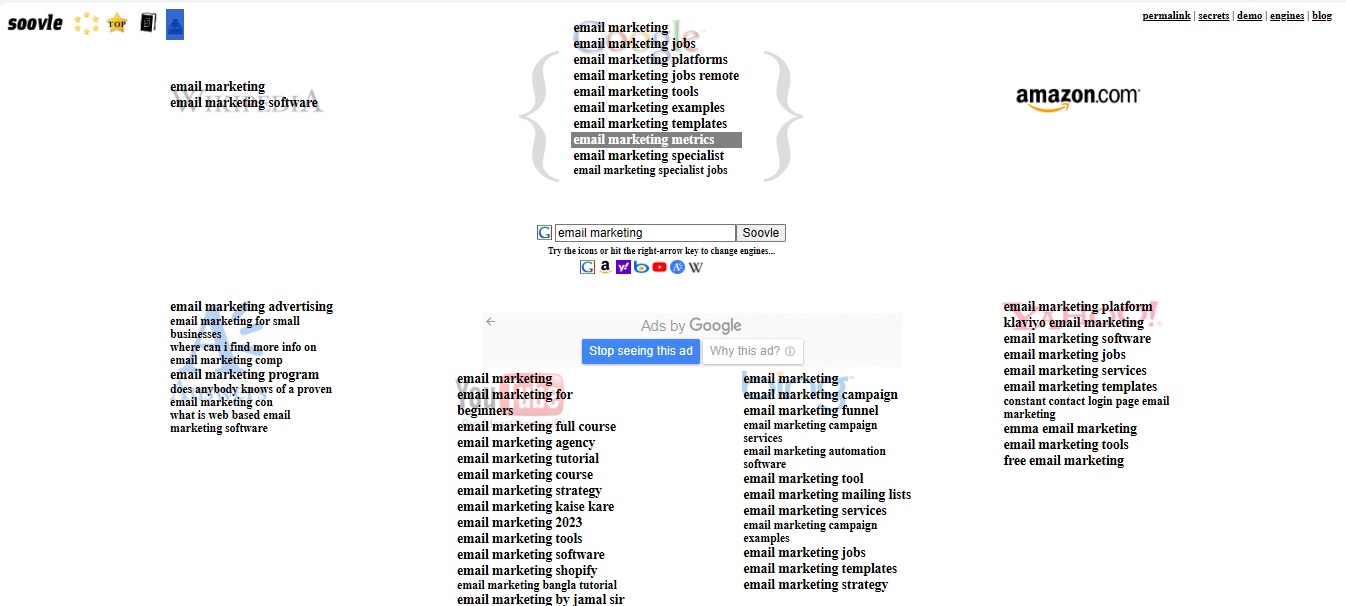
Find Trending Topics
Yet another popular method to generate keyword ideas is finding trending topics on Q&A sites like Reddit and social media platforms such as Twitter, Facebook, etc.
BuzzSumo is a great tool to find top-performing content across the web. You can use its content analyzer feature to find the most shared content across platforms like Reddit, Facebook, Twitter, and Pinterest.
Research Competitors
An essential keyword research component is investigating competitors to learn about keywords that generate traffic to their sites. However, before you can investigate competitors, you must first identify them. An excellent way to identify competitors is to type seed keywords in the Google search bar and look at the sites that rank on the first page.
Another great way to find competitors is to search for top blogs or sites related to your niche. For example, you can search for 'best tour services' if you offer tourism services.
Once you have identified your competitors, you can investigate their websites to see what keywords they are targeting. However, with manual investigation, you may not discover the top pages that bring the most traffic. Additionally, it would be challenging to get the complete list of keywords that the web pages rank for.
Therefore, I suggest using a keyword research tool to identify and inspect competitors' websites. For example, in UbberSuggest, if you click on the 'similar websites' under the 'keyword research' tab in the side menu, you will get a screen where you can enter your website to get a list of similar websites.
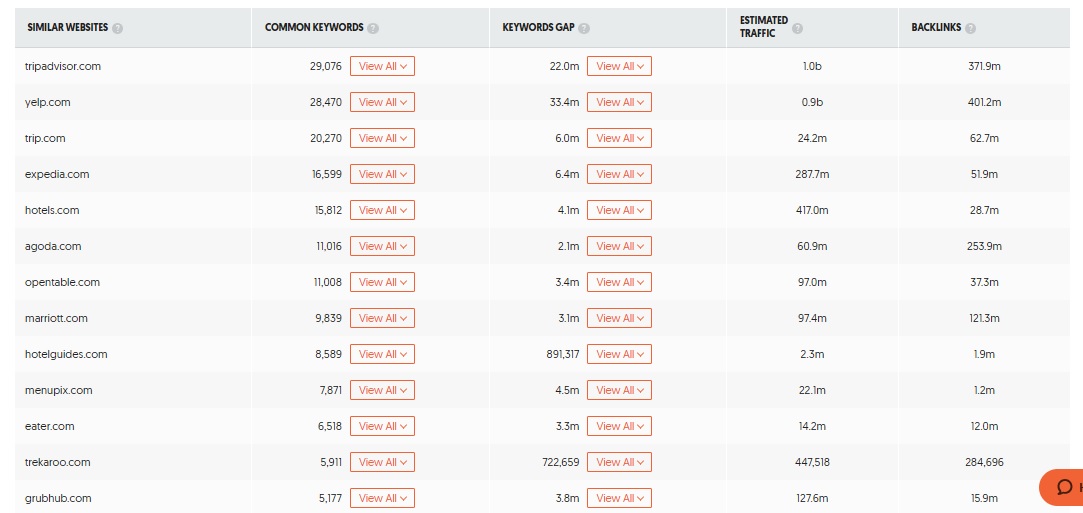
As shown in the screenshot above, UbberSuggest provides a list of common keywords your website and the competitor website rank for, along with the keywords gap. If you click on keywords gap, you will get an exhaustive list of keywords your competitor ranks for, but you don't.
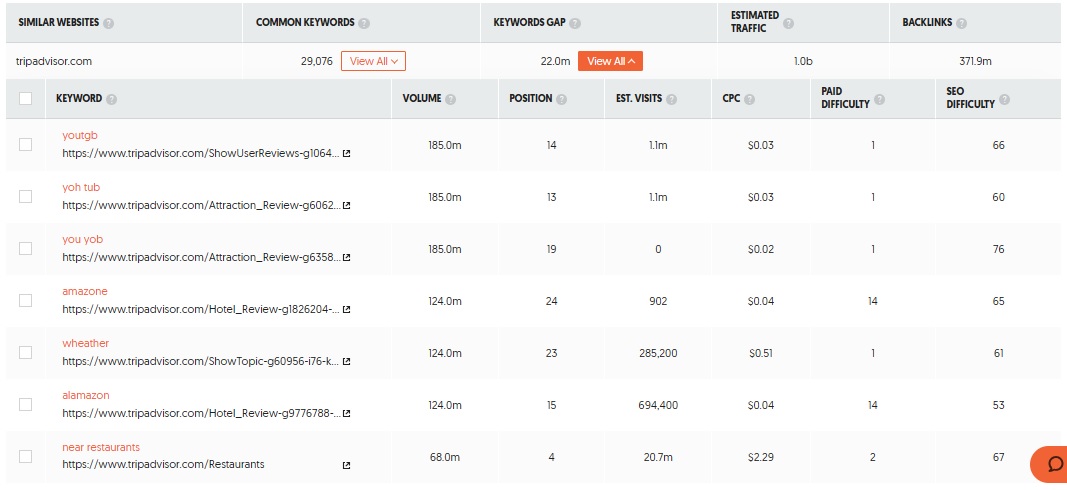
For each keyword, you can see the monthly search volume, estimated visits, rank in Google search, and SEO difficulty, i.e., estimated competition in organic search. Later in this post, I will discuss why you need search volume and search difficulty to choose keywords. At the moment, the purpose of researching competitors is to generate keyword ideas.
Utilize Google Search Console
Using Google Search Console, you can find out what queries people use to get to your website. Many of those queries may have high search volume, and incorporating them into your content can generate additional traffic.
To find out the keywords or key phrases people use to get to your site:
- Click on the 'performance' tab on the right side.
- Scroll down and click on the 'pages' tab to get the list of pages that rank in Google search results.
- Choose and click on any page and click on the 'queries' tab to get the complete list of search queries for which the web page ranks.

Make a list of queries with a high number of impressions but a low number of clicks. Alternatively, you can list queries with an average position above 10, i.e., the queries for which your page does not rank on Google's first page. After making the list, use those key phrases in your post a reasonable number of times to increase your rank and number of clicks for the keyword.
Step 2: Analyzing Keywords
Now that you have hundreds of keyword ideas, it is time to shortlist keywords that will benefit you the most. To determine the best keywords for your business, you should consider the following factors:
Search Volume
The average number of times Google searchers use a particular keyword to find information online is referred to as search volume. A high search volume keyword will likely bring more organic traffic to your site, but is harder to rank for. On the other hand, a low search volume keyword will generate less traffic but is easy to rank for.
There is no hard and fast rule related to search volume. Depending on your niche, you can decide a good search volume a keyword must generate to qualify.
You can use a keyword research tool, such as SEMrush, Serpstat, SpyFu, and UbberSuggest, to determine the search volume.
Below is a screenshot of the keyword overview in SEMrush, showing the search volume:
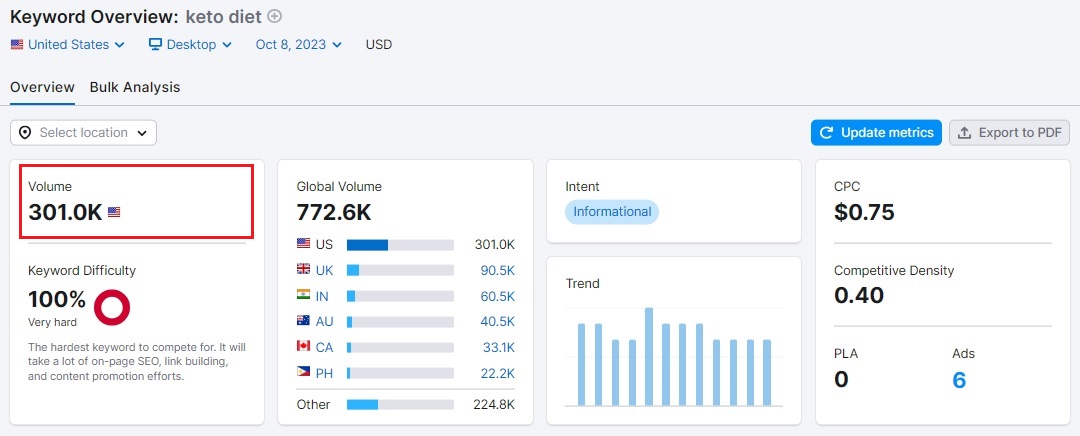
You can change the location based on your target audience's demographics.
Search Difficulty
Search difficulty is a metric indicating how difficult a keyword is to rank in Google search results. A high search difficulty means the keyword is highly competitive, while a keyword with low search difficulty is easy to rank for.
Like search volume, you can determine search difficulty using keyword research tools. For example, the following screenshot shows keyword difficulty in SEMrush.
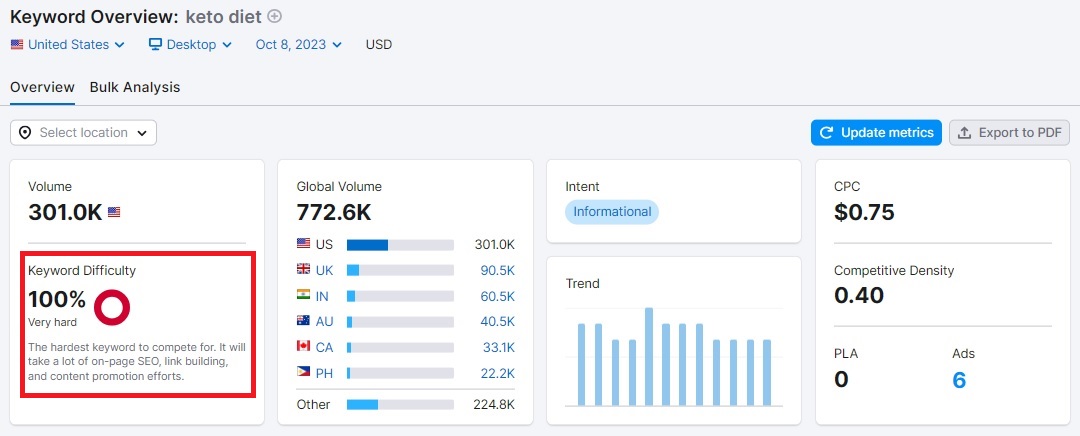
However, if you are low on budget and don't have access to any tool, you can determine the difficulty of keywords using Google search. Type the keyword in Google search and analyze the top 10 sites in search results. If the average domain of the top 10 websites is high, the keyword has high search difficulty. To determine the domain authority of any site, you can use Moz's free domain authority checker.
As a rule of thumb, you should target keywords with low search difficulty if your website is not older than six months. With time, you can target keywords with relatively higher search difficulty.
Therefore, for new websites, I suggest targeting long-tail keywords. You can get long-tail keyword ideas using tools like KWFinder and LongTailPro.
Cost Per Click
For effective keyword research, consider cost per click or CPC. A keyword for which businesses spend money is worth targeting, regardless of their search volume. For example, a keyword with a relatively low search volume but a high CPC is worth targeting. The below screenshot shows CPC in SEMrush's Keyword Overview Tool.
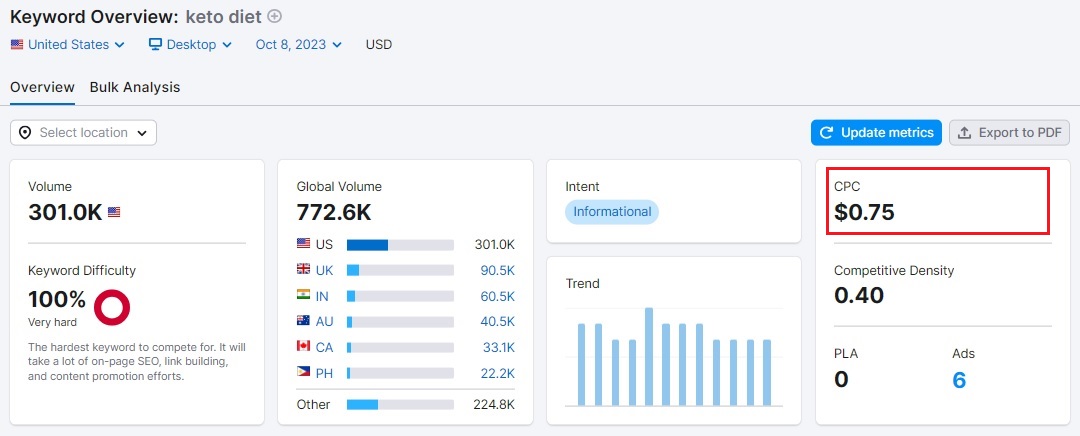
SEMrush also allows bulk keyword analysis. This feature is useful when comparing multiple keywords for search volume, difficulty, and CPC. You can enter up to 100 keywords in SEMrush's Keyword Overview Tool, as shown below.
Keyword Trend
Another essential factor for keyword research is trend or search interest over time. The search volume only indicates the estimated monthly searches the keyword generates. It does not tell anything about how the keyword has performed in the past. In other words, it does not indicate the trend the keyword has followed over time.
Using Google Trends, you can learn if the keyword has gained or lost popularity over time. A keyword with a low search volume but gaining popularity is good for targeting. On the contrary, a keyword with high search volume but declining search interest may not benefit you in the long run.
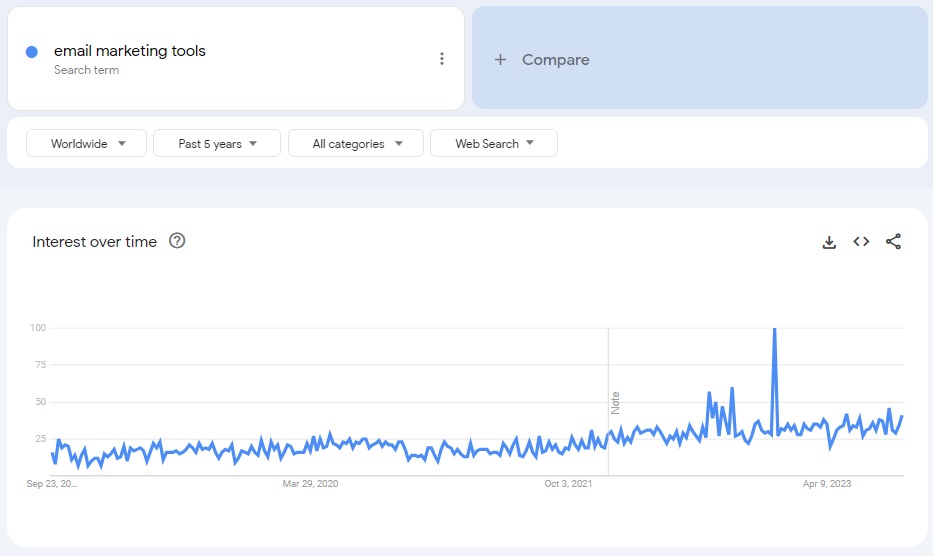
As shown in the screenshot above, Google Trends allows you to choose the period for which you want to analyze the trend. You can also select a country or check the worldwide trend.
Step 3: Targeting Keywords
The most critical step of keyword research is to use the keywords in a way that can benefit you the most. In other words, you should incorporate keywords in your content in a way that helps you rank higher in SERPs. Targeting keywords requires you to identify primary and secondary keywords and research search intent, as discussed below.
Identify Primary and Secondary Keywords
Before creating content around keywords, it is crucial to identify primary and secondary keywords for the content.
A webpage or content can rank for multiple keywords, but only one focus keyword represents the topic of the content. The focus or primary keywords have the highest search volume among all keywords. It appears in the title, URL, and H1.
On the other hand, secondary keywords have a relatively low search volume and constitute the subheadings of the content. For example, 'email marketing' is the primary keyword, while 'benefits of email marketing', 'how to do email marketing', and 'email marketing history' are secondary.
Identifying primary and secondary keywords serves two purposes:
- It helps create topic clusters. In topic clusters, you create a main post, i.e., pillar content covering the topic in a broader aspect, while for each subheading or subtopic, you create an individual post, i.e., cluster content. Using internal links, you link pillar content with clusters. Topic clusters or content clusters help build topical authority and improve the structure of your website.
- It helps assist in content creation.
Research Search Intent
Your keyword research efforts can fail if you do not research the search intent of the primary keyword. Google will only rank you higher for a particular keyword if the content matches the search intent.
Search intent refers to the kind of content a user expects when searching on Google using a keyword. Since Google aims to provide the best experience to its users, it ranks content based on its relevance to the search intent.
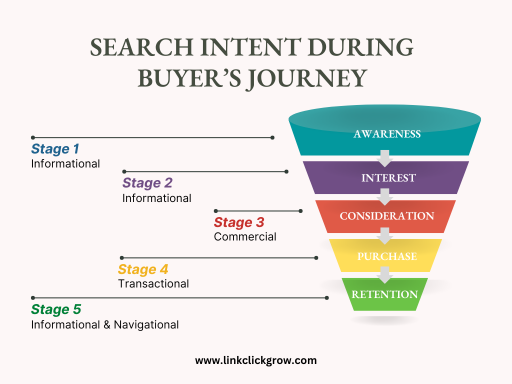
The following are the four basic types of search intent:
Informational: If the searcher expects information, answers, or knowledge-based content, the search intent is informational. What, how, and why posts, such as tutorials and guides, are informational.
Navigational: If the searcher is looking for a specific brand, business, website, or webpage, the intent is called navigational. Keywords or key phrases that include brand or product names are navigational.
Commercial: Commercial intent means the searcher wants to learn more about available products or brands to help make purchase decisions. List posts, comparison posts, and reviews have commercial intent.
Transactional: The intent is transactional if the searcher wants to purchase a product and is looking for the best deal or policies related to the purchase. Transactional intent keywords usually include words like 'buy', 'discount', 'coupon', 'cheap', 'download', 'sign up', and 'register'.

You should target keywords and create content according to their search intent. Below is how each stage of the customer journey aligns with search intent.
However, if you need clarification on the search intent, you should check the content Google ranks on the first page for that particular keyword. Carefully examine the top ten web pages to discover the search intent and create content in a similar format.
Conclusion
Organic traffic is the most reliable source of traffic that offers long-term benefits. However, you can generate organic traffic only if your content is optimized for keywords, terms, or queries people use to find information online. That is why keyword research is the strongest pillar of SEO. Keyword research helps you rank higher and satisfy target audience needs by targeting the right keywords in the content.






0 Comments